Sugar Cane
Overview
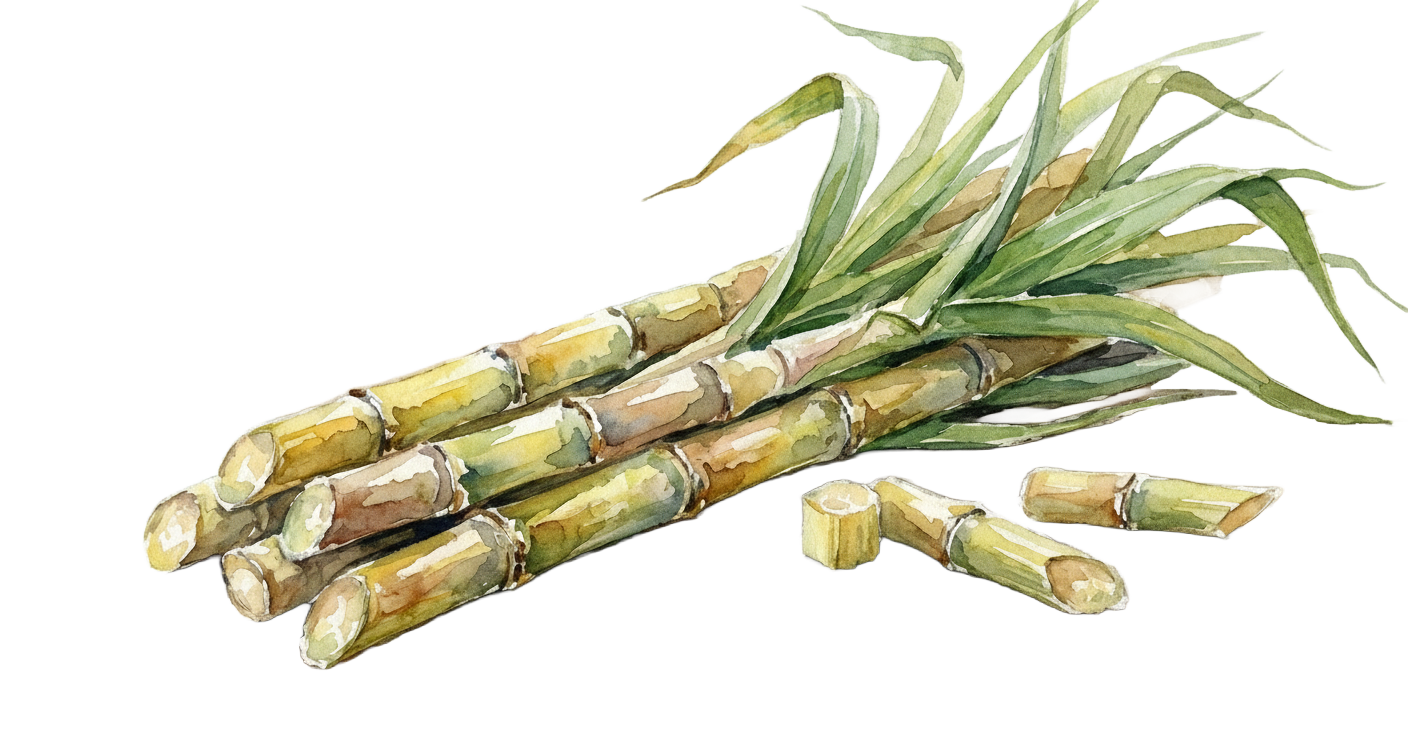
The plant contains high concentrations of sucrose stored in its thick, jointed stalks.
Rich in carbohydrates and essential minerals, sugar cane and its derivatives supply energy, support digestive health, and are used in food, beverages, livestock feed, and renewable energy industries.
Originating from Southeast Asia and the Pacific region, sugar cane thrives in warm, humid climates with abundant sunlight and moisture. The main region for growing is the tropical and subtropical belt, Brazil is the largest sugar cane producer.
It is typically propagated vegetatively through stem cuttings and grows as tall clumps with an extensive fibrous root system that helps anchor the plant and support vigorous growth.

Soil
Sugar cane performs best in well-drained, fertile soils such as loams or clay-loams with high organic matter. The ideal pH ranges from 6.0–7.5
Irrigation
Drip or furrow irrigation is commonly used, ensuring uniform water distribution throughout the long growth cycle
Temperature
Optimal growth occurs between 25°C and 35°C
Light
Full sunlight is required for strong photosynthesis and high sugar content. Shaded conditions reduce stalk growth and overall sucrose accumulation
Global Production