Blueberries
Overview
They are characterised by exceptionally high nutritional value, including a notable concentration of anthocyanins – natural pigments responsible for their blue-purple colour and their strong antioxidant properties.
These compounds help reduce inflammation, support heart health, improve visual function (especially night vision), and slow cellular ageing processes. In addition, blueberries are rich in dietary fibre, vitamin C, vitamin K, and essential minerals.
The shrub has a shallow root system and is adapted to highly acidic soils – a trait that limits cultivation to certain climate zones and requires careful soil management. Some cultivars are deciduous and require a prolonged chilling period to break dormancy, while others are evergreen and suited to milder climates.
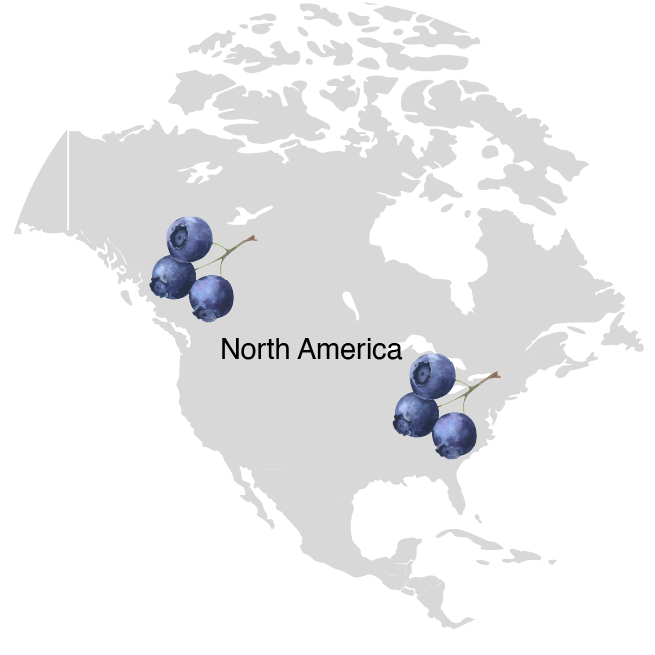
Blueberries grow naturally in wetland areas and on moist slopes in North America, but with advances in cultivation methods, planting in acidic growing media, and precise irrigation technologies, they have become a significant commercial crop worldwide. Strong global demand stems from the combination of delicate flavour, high nutritional value, and versatile uses in both the fresh market and the food industry.
Soil
Highly acidic soils (pH 4.5-5.5), well aerated and rich in organic matter; highly sensitive to lime (calcareous conditions) and salinity
Irrigation
Continuous drip irrigation and maintaining uniform moisture; avoid saturation due to the shallow root system
Temperature
Optimal range: 16-25°C. Highly sensitive to frost during flowering and to extreme heat
Light
Full sun is required for colour development, sugar accumulation, and fruit quality
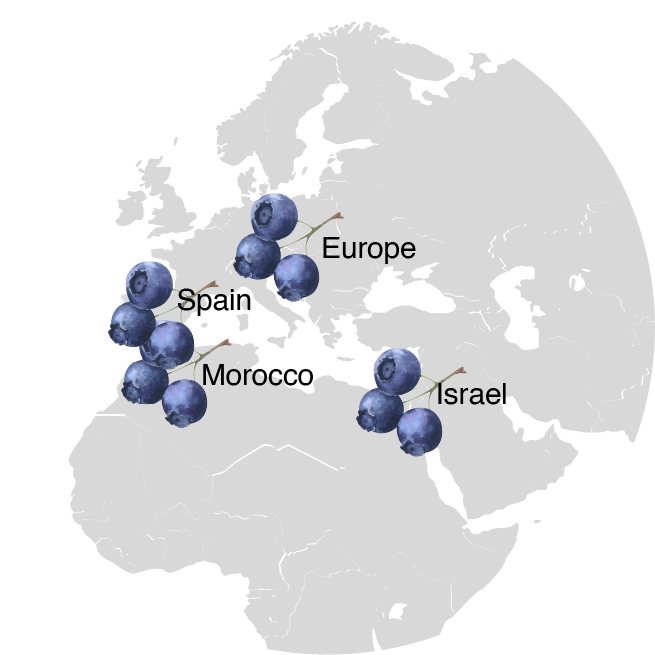
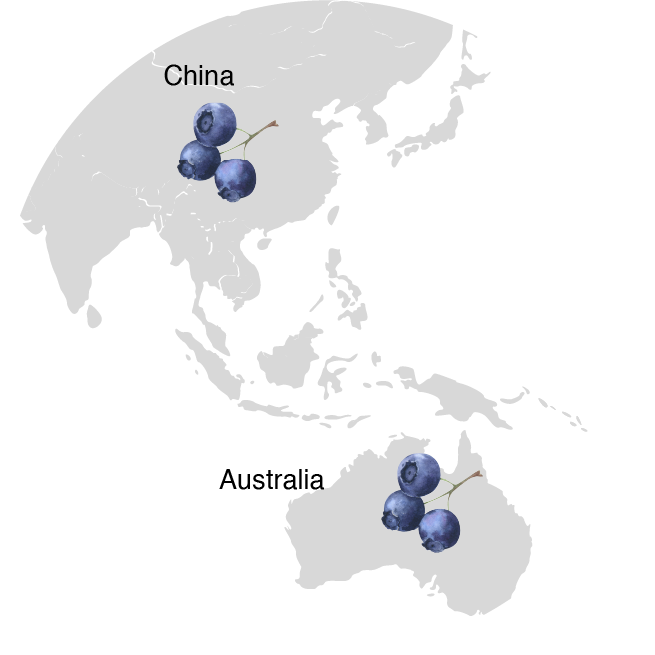
Global Production
Blueberry Articles

Blueberry Nutrition- The Latest Hit
Blueberry is considered a "superfood", for its many health properties and nutritional values including vitamins, minerals, trace elements, powerful antioxidants, and fibers. Blueberries Anthocyanins (purple/blue dye color) are powerful antioxidants also used as anti-inflammatory substances. These same substances contribute to cardiovascular health, while also improving and maintaining optic health and enhance vision, especially night vision.

