Tomatoes
Overview
It is characterised by a rapid growth rate, the ability to adapt to both greenhouses and open fields, and a self-pollination mechanism in most cultivars – a significant advantage for achieving a uniform yield.
The fruit is a fleshy, multi-seeded berry that appears in a wide range of shapes and sizes: cherry tomatoes, cluster (truss) tomatoes, medium-sized tomatoes, and large, meaty varieties. This diversity of cultivars enables adaptation to both fresh markets and processing industries, including the production of tomato paste, purees, ketchup, and canned products.
Nutritionally, tomatoes are considered among the healthiest foods: they are rich in lycopene – a powerful antioxidant associated with reduced risk of heart disease and cancer – as well as vitamin C, potassium, and folic acid.
Thanks to cultivar development, precise irrigation management, and advanced greenhouse cultivation, tomatoes have become a leading global crop adapted to a wide range of climates.
Soil
Light to medium soils, well drained; sensitive to excessive salinity
Irrigation
Precise drip irrigation, maintaining low moisture fluctuation
Temperature
Optimal range: 18-28°C. Highly sensitive to frost/cold and extreme heat
Light
Full sun; essential for photosynthesis and lycopene accumulation
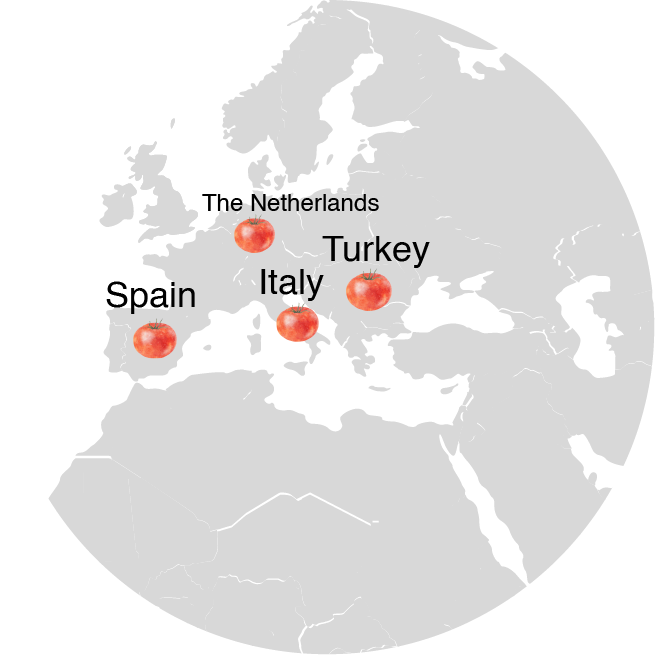
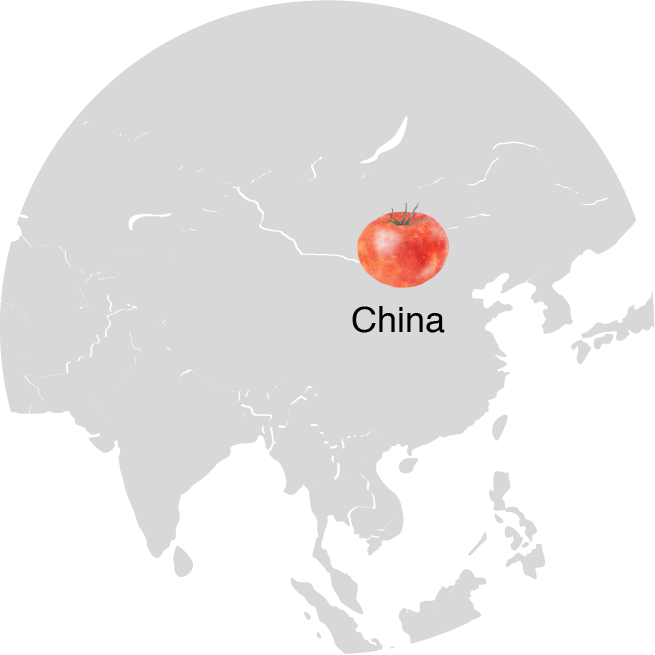
Global Production


Tomato Articles

Magnesium deficiency in greenhouse tomatoes
Magnesium is an important plant nutrient and is one of the macro elements required for plant nutrition. It is localized to the center of the chlorophyll molecule, and it functions as a cofactor in different enzymatic reactions essential for different aspects in homeostasis like sugar synthesis and solutes movement.

Growth Stages
Establishment (0–2 years) – Root and shoot development. Sensitive to salinity and poor drainage. Vegetative Growth (spring) – Leaf canopy and shoot elongation determine fruiting potential. Flowering & Fruit Set (late spring) – Adequate Nitrogen and Phosphorus are essential for flower differentiation and fruit initiation.

Sustainability Focus
A short description of the service and how the visitor will benefit from it.

