Avocado
Overview
Botanically, avocado is characterised by a shallow root system that is active mainly in the upper soil layer, making it particularly sensitive to oxygen deficiency and salinity.
The tree is divided into three main genetic races – Mexican, Guatemalan, and West Indian – whose combinations produced most commercial cultivars, foremost among them the ‘Hass’ variety.
Flowering is characterised by a unique two-day opening and closing mechanism (Type A/B), which affects pollination efficiency; therefore, complementary cultivars are sometimes planted within the same orchard.
Avocado is considered a food with exceptionally high nutritional value: it is rich in monounsaturated fats, potassium, B vitamins and vitamin E, as well as antioxidants and phytochemicals that support heart and digestive health.
The tree is suited to warm subtropical climates with mild winters and is highly sensitive to frost. Thanks to advances in fertilisation, precise irrigation, and the development of resilient rootstocks, avocado has become one of the fastest-growing fruit crops in the global market.
Soil
Well drained soil, free of waterlogging; highly sensitive to salinity and calcareous (lime-rich) conditions
Irrigation
Precise, frequent irrigation; avoid excess water
Temperature
Optimal range: 18-28°C; highly sensitive to frost
Light
Full sun; light shade in particularly hot areas
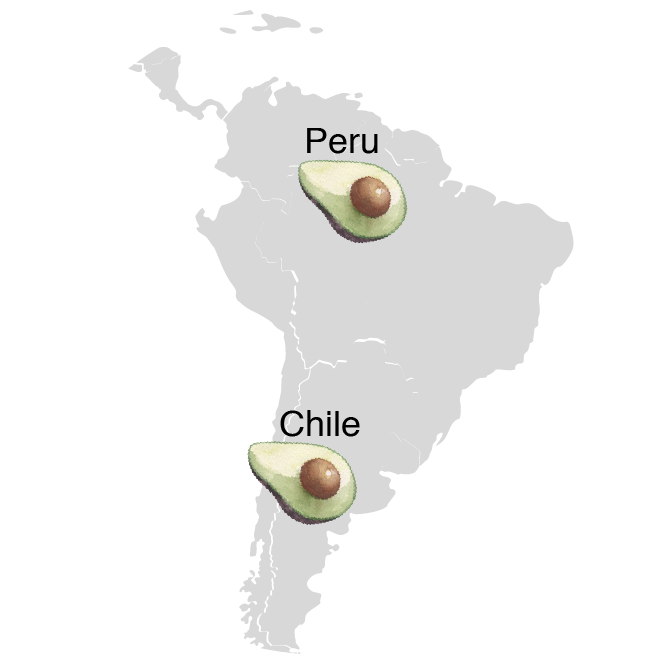
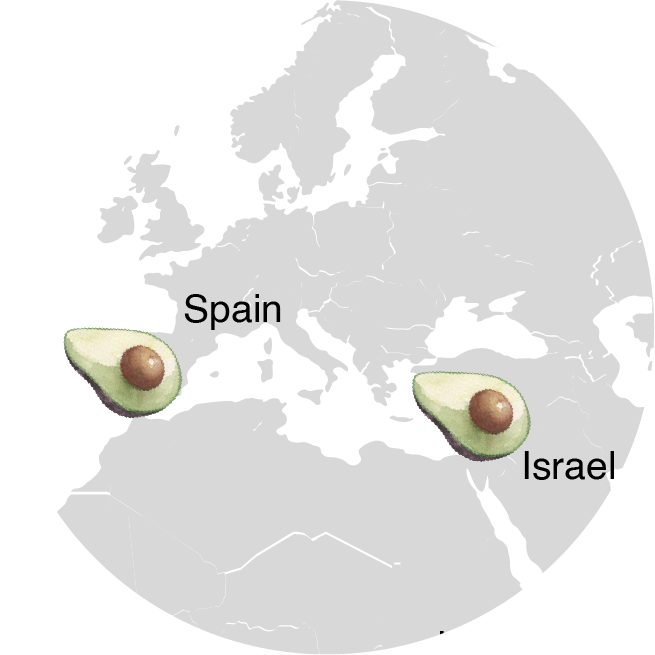
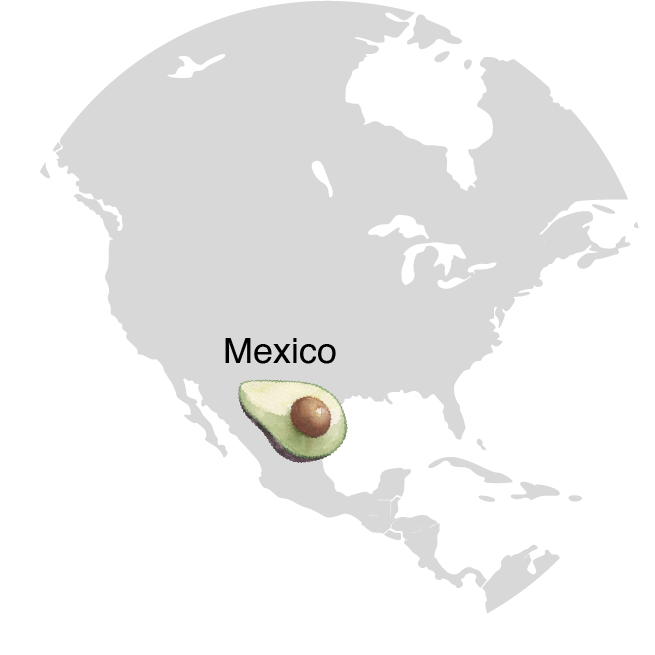
Global Production
Avocado Articles

ZincGat Chelate in Avocado fertigation – it works!
Zinc (Zn) is absorbed by the plant as the cation Zn2+, which is dissolved in the soil solution. Zinc is one of the microelements essential to plants in general, and particularly for avocado. Research has shown that zinc is necessary for growth processes and protein synthesis.

Advantages of Fertilizing Avocado with Biostimulant Additives
The “hot news” in plant nutrition is fertigation with biostimulants, as additives to traditional fertilizers.

Avocado Fertilization with Gatit Blue
The avocado is a subtropical cultivar originally from Central America. Brought to Israel in the early 20th century, but commercial cultivation began only in the 1960s.

